Get started with APEX AIOps Incident Management
Try the interactive demo
Customers, partners, and Dell Technologies employees can log in to the Dell Technologies Demo Center and try out the APEX AIOps Incident Management online interactive demo.
Are you new to APEX AIOps Incident Management? Review the following sections to begin your AIOps journey.
The following diagram shows how data flows into Incident Management and how it's processed:
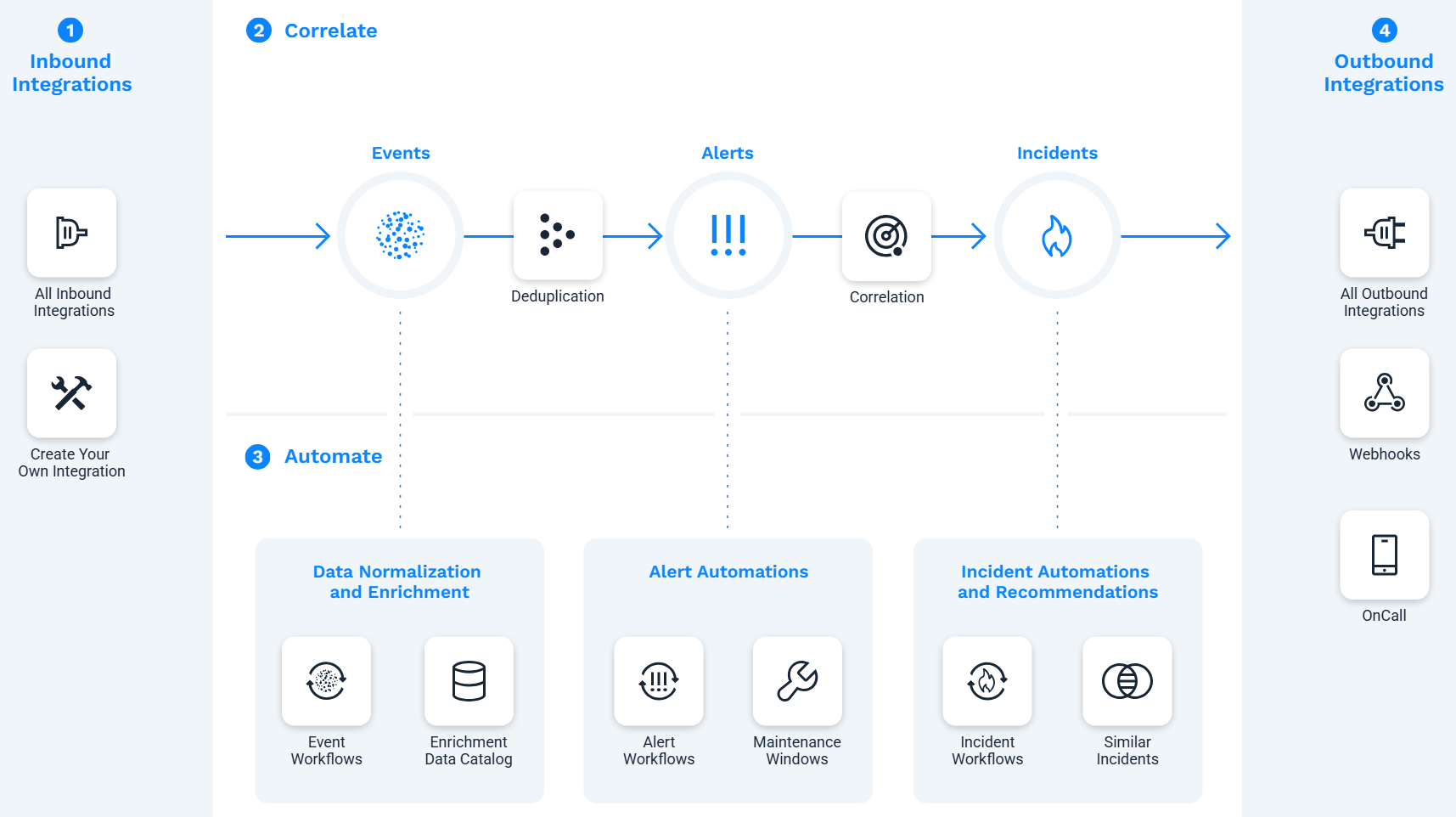 |
Continue reading through the sections below for information on achieving each step.
 |
 |
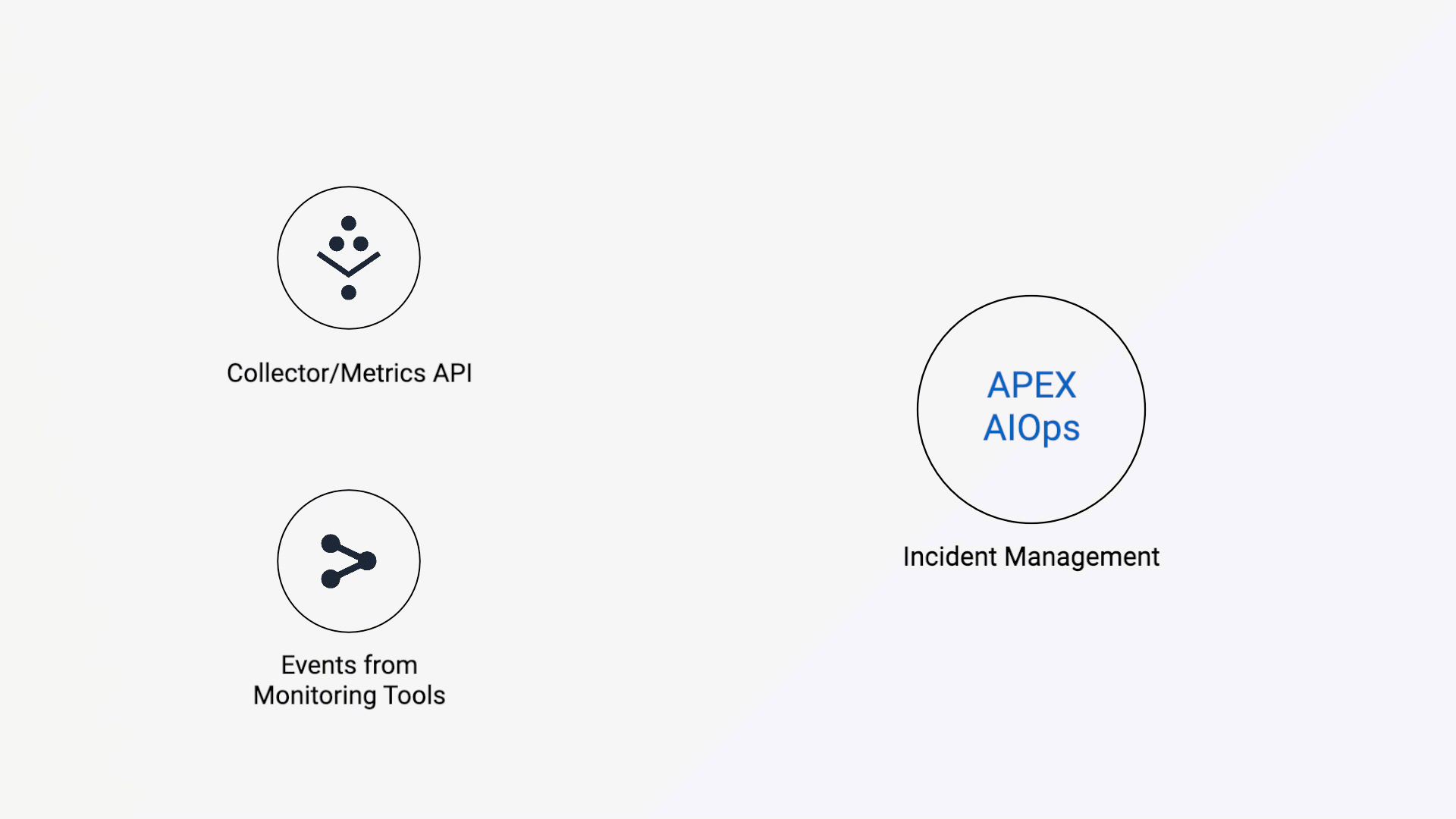
The first step to realizing the value of AIOps is getting data into your instance.
Incident Management supports data ingestion using three methods:
Collectors installed on external systems
Choose from a variety of plugins to collect data from Linux, MacOS, and Windows systems.
Inbound integrations with target systems
Incident Management supports a wide array of integrations with external systems.
Custom integrations
Don't see your external system in the list of integrations? You can still ingest data using another method:
After you have data coming into your instance through ingestion, you'll want to create meaningful incidents by first enriching events with key data, and then consolidating events into representative alerts.
A key objective in this phase is to reduce noise.
 |
 |
This goal is achieved through these activities:
Normalize and enrich data
Use event workflow to add important information to events to build alerts containing the information you need.
Deduplicate data
Combine similar events into representative alerts to reduce information overload.
Correlate alerts into incidents
Use alerts to build and surface context-rich incidents which present clear pictures of issues, allowing support teams to troubleshoot and resolve them efficiently.
Resources
Refer to the following topics for detailed information on the concepts in this section:
Normalize event data | |
Enrich events | |
Deduplicate data | |
Correlate alerts into incidents |
Automation is a key component of AIOps at nearly every level. Incident Management automates numerous tasks, at the event, alert, and/or incident level. In fact, when you have completed Step 2, you are already well on your way to automating many labor-intensive tasks.
Event, alert, and incident workflows
In addition to the automation baked in to Incident Management, you can automate many manual tasks by configuring workflows, such as:
Assign users to alerts and incidents
Add, remove, or otherwise manipulate the data in alert and incident fields
Assign a group to alerts and incidents
Change the Priority, Severity, or status of an alert or incident
Add comments and send an email to interested users
Maintenance windows
When service interruptions are planned, you can schedule maintenance windows to handle alerts arriving during that time differently, or simply add the information to the alert.
Similar incidents
Over time, Incident Management gathers historical information and indicates which current incidents resemble past incidents via Similar Incidents. Add resolving steps to your incidents, and you can troubleshoot current incidents the same way as similar incidents in the past.
Resources
Refer to the following topics for detailed information on the concepts in this section:
Workflows | |
Maintenance windows | |
Similar incidents |
When your incident data is correlating correctly and includes the right information, consider how you would like to use it.
Outbound integrations
When alerts and incidents appear the way you want them to, you can send them to external systems. This is an optional step, but one that can be invaluable if you have an external system that you need to keep in sync with the activities which occur in Incident Management.
OnCall
Build customized rotating schedules and notification policies to keep the right people informed when critical issues happen.
Note
Contact Dell Support for details on adding OnCall to your Incident Management instance.
Resources
Refer to the following topics for detailed information on the concepts in this section:
Webhook endpoints | |
PagerDuty | |
Performing outbound tasks | |
OnCall |