Moogsoft Hybrid Integration Installation
Description
This integration provides a single location to configure the endpoints and payloads that the sendToCloud function uses.
This integration consists of the following sections:
Moogsoft Cloud Endpoints
Payload Maps
The Endpoints section consists of a simplified version of the standard REST Endpoints integration, removing the Headers, Security and Proxy settings. The Payloads section has the same base functionality as the Payloads integration, with some predefined mappings for Moogsoft Onprem (Onprem) to Moogsoft Cloud (Cloud) event schemas. Additionally, the payload is split into mandatory and optional fields to ensure that any event payload sent from Onprem to Cloud has the minimum schema populated.
Important
This integration is not designed as a permanent, persistent architecture from Moogsoft Onprem to Moogsoft Cloud.
It is designed as an accelerator, to allow existing Onprem users to adopt or test Moogsoft Cloud without the need to change event ingestion processes.
It is designed to bridge identified functional gaps between Onprem and Cloud while Cloud functionality matures and reaches parity with Onprem.
This use case should be discussed with Moogsoft support before implementation.
Once parity with Onprem is reached, this integration will no longer be supported.
What and when to export?
The Moogsoft Hybrid integration and associated sendToCloud function allow Moogsoft Onprem (Onprem) to send events to Moogsoft Cloud (Cloud). Although the integration and function do not prevent exporting Situations as events to Cloud, the use cases for doing so are limited. In general, either events or alerts are exported.
Export events when there is no requirement for additional alert-level processing in Onprem.
For example, where an event source cannot be ingested by Cloud directly.
NOTE: This is used primarily in the adopt or test the Onprem to Cloud use case.
Export alerts when there is a requirement for the event in Cloud to have the benefits of Onprem processing, notably:
Entropy
Enrichment (where this cannot be performed in Cloud)
Maintenance windows
This is used primarily in the functional bridge Hybrid use case.
In this use case, Onprem does not perform any correlation; all correlation occurs in Cloud.
Events would be exported via the Event Workflow Engine; alerts generally via the Alert Workflow Engine. Where this integration is used for parallel Onprem and Cloud operations (for example, when adopting or testing Cloud), then a separate Export Workflow engine is recommended to ensure that no export backlog impacts Onprem functionality.
Installation
The integration is installed via the UI, but also requires an additional Inform-based workflow engine to be added to the moog_farmd.conf configuration file. The Moolet configuration file (cloud_inform_workflows.conf) is bundled with the WFE bundle, but the manual step of adding this to the configuration file and starting the Moolet should be performed before installing the integration.
In the moog_farmd.conf file, add the following line in the moolets section (add a comma at the end of the line, if necessary):
{ include : "cloud_inform_workflows.conf" }After you add the line, restart the Moolet using either farmd_cntl, or by restarting moog_farmd.
Note
Make sure you change this configuration for both the primary and secondary moog_farmd servers, and that the Moolet is restarted on both.
Configuration
Endpoint configuration
A Moogsoft Cloud endpoint has the following configuration items:
Configuration item | Required? | Description |
|---|---|---|
name | yes | The unique name for this endpoint; for example, Prod. This is referenced in the |
Events API URL | yes | The Cloud API endpoint the export is sent to. Generally, this is the Events API, but could also be a Create Your Own Integration endpoint. |
API Key | yes | The API key to use in the export. This API Key needs to have sufficient privileges to use the endpoint specified in the Events API URL. |
Send Heartbeat Alert | no | A checkbox. When this box is checked, Moogsoft Onprem sends a heartbeat event to the Cloud endpoint every 60 seconds. |
Multiple Cloud endpoints can be configured within the same integration, allowing events to be multiplexed to different Cloud environments using multiple sendToCloud workflows. For example, you could send a subset of Onprem events to an Cloud QA system for testing.
Heartbeat alerts
The 2.4 Add-Ons includes a bundled 2.4Scheduler.js (under $MOOGSOFT_HOME/bots/moobots) and a corresponding Moolet configuration, scheduler-24.conf (under $MOOGSOFT_HOME/config/moolets).
The Scheduler Moobot contains the functions for the Cloud integration and the Retry Queues integration (delivered as part of Add-Ons 2.3.5).
If the heartbeat alert functionality is required, then the Add-Ons 2.4 Moobot / configuration needs to be merged into any existing Scheduler Moobot.
Payload map configuration
A payload has the following configuration items:
Configuration item | Required? | Description |
|---|---|---|
Name | yes | A unique name for this payload map. This is referenced in the |
Convert Custom_info to tags | no | A checkbox. When checked, the entire |
Mandatory fields | yes | A set of mandatory fields that must be mapped for the export to be successful. |
Optional fields | no | A set of mappings for additional fields (such as tags, location, class) that can be added as needed. |
Multiple payload maps can be configured within the same integration, allowing differential mapping of Onprem source events to a normalized Cloud event. This scenario uses multiple sendToCloud workflows. For example, if two Onprem events had different custom_info fields representing the location of the event, two export workflows could be used, each using a different payload map—allowing the different Onprem schemas to be normalized to a single Cloud schema.
Default mapping
When the integration is installed, a default payload map (AlertMap) is added. This payload map contains the following mandatory mappings:
Cloud schema name | Mapped Onprem value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| $(signature) | |
| $(source) | |
| $TO_INT(severity) | |
| $(description) | |
| $(agent)::$(manager) | |
| $TO_JSON([ ]) | This is an empty list. Replace it with the Onprem field containing a list of services. |
| $TO_INT(int_last_event_time) | If preferred, $(moog_now) can be used to impose the export time on the outbound event. |
| $TO_FLOAT(entropy) | Sends a floating point value for entropy. |
|
| Sends the current value of the alerts maintenance status. This mapping should match the |
Changes to these mappings are allowed, but Cloud rejects the event when these mappings are not populated, or if the data is of the wrong type (as when sending a severity as text instead of an integer value). Macro mapping is supported in this payload, so you can use $EXPAND() and other macros as needed.
Optional mapping
Optional mapping allows non-core fields to be added. When adding an optional field, select the field from the available drop-down list, and supply an Onprem value and a default value (if needed). The default value is used if the Onprem event does not have a mapped value.
Tags
When adding a tag, the tag name can be nested (deep), but the resulting tag will be flat. For example, in the tag name below, we have “test.test1.test2” which results in a tag on the Cloud event of:
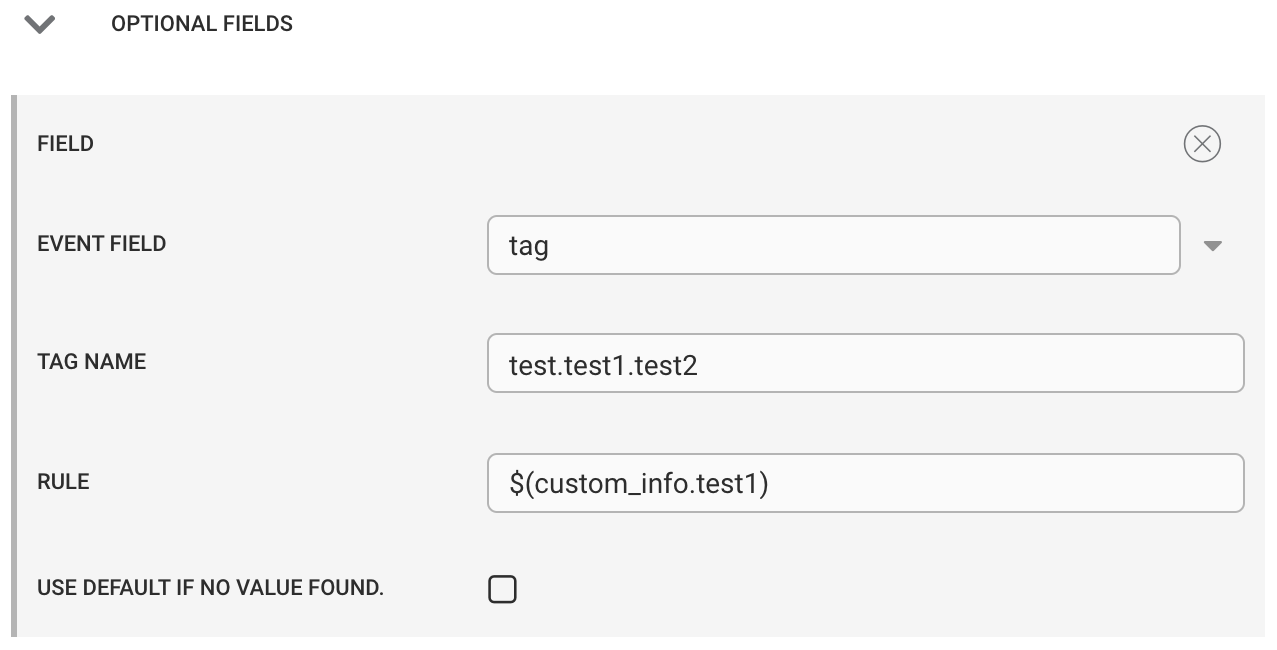 |
The tag name above is “test.test1.test2,” which results in a tag on the Cloud event of:
tags : {
"test.test1.test2" : <value of custom_info.test1>
}and not
tags : {
test : {
test1 : {
test2 : <value of custom_info.test1>
}
}
}Tags in Cloud are single-depth key:value pairs.
Location
When adding location mappings, a deep object is created:
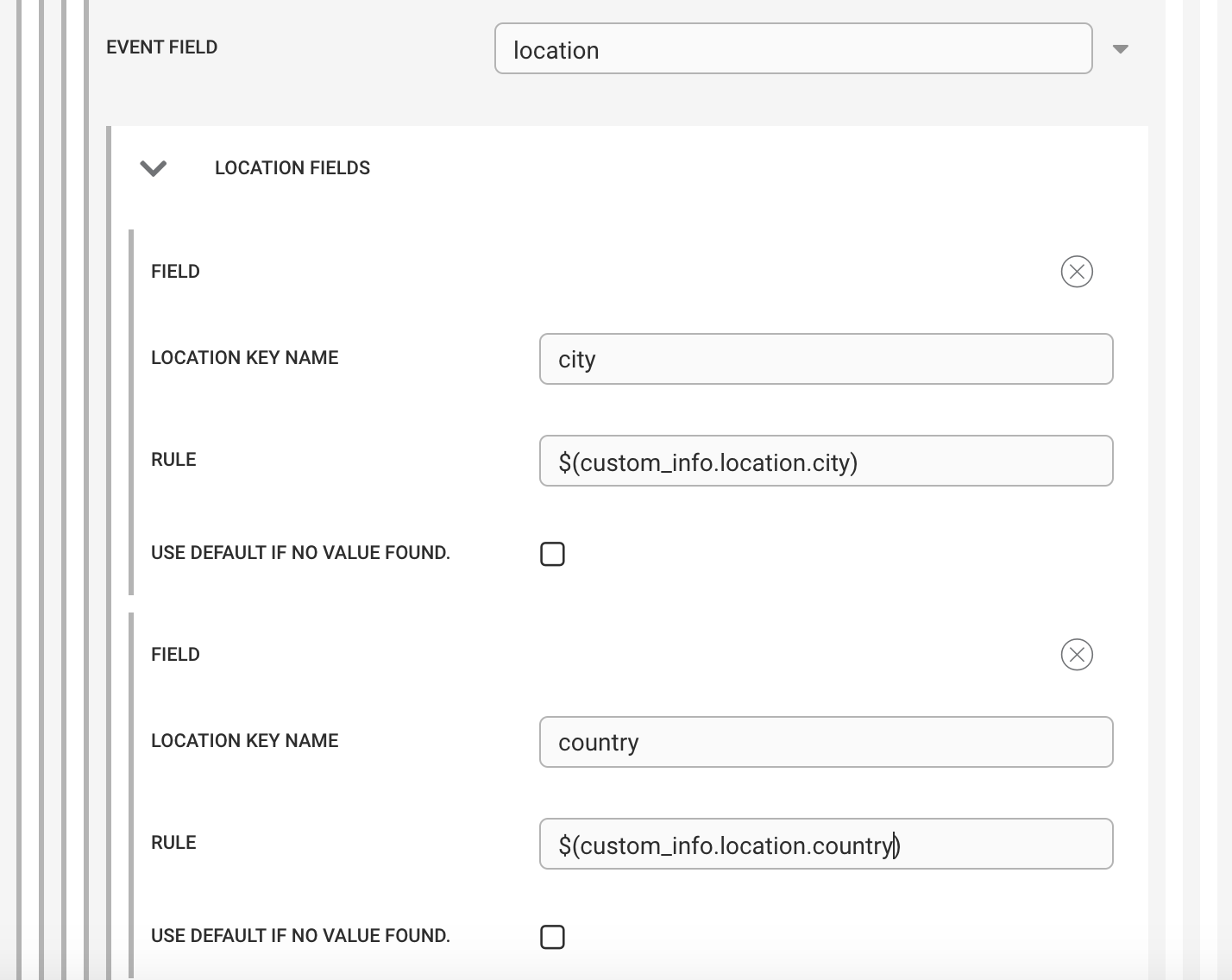 |
In the above example, the resulting object in Cloud is:
location : {
city: <value of custom_info.location.city>
country: <value of custom_info.location.country>
}Using the generic workflow actions
The Moogsoft Hybrid integration and sendToCloud function perform the same purposes as a set of generic WFE functions, but as a convenient single integration and function. If the functionality of these tools does not meet a requirement (for example, if complex payload manipulation is required before dispatch), then you can perform the following steps to achieve the same behavior:
Define your target Cloud system in the REST Endpoints integration.
Ensure the apiKey is added as an additional header.
Define your event payload in the Payloads integration.
Ensure that the core fields are mapped appropriately and any additional fields are of the correct type (specifically
tagsandlocation).Define Retry Queue for retries to be attempted (recommended):
Create an Export workflow:
getPayloadfunction referencing the Payload configurationconvertCustomInfoToTagsfunction, if requiredcopyToPayloadfunction to copy the flattened tags from theworkflowContextto the outbound payload.exportViaRestWithRetryfunction referencing the REST endpoint configuration and Retry Queue configuration.