Set Up the Core Role for HA
In Moogsoft Onprem HA architecture, Core 1 and Core 2 run in an active / passive HA pair.
HA architecture
In our distributed HA installation, the Core components are installed on Core 1, Core 2, and Redundancy servers:
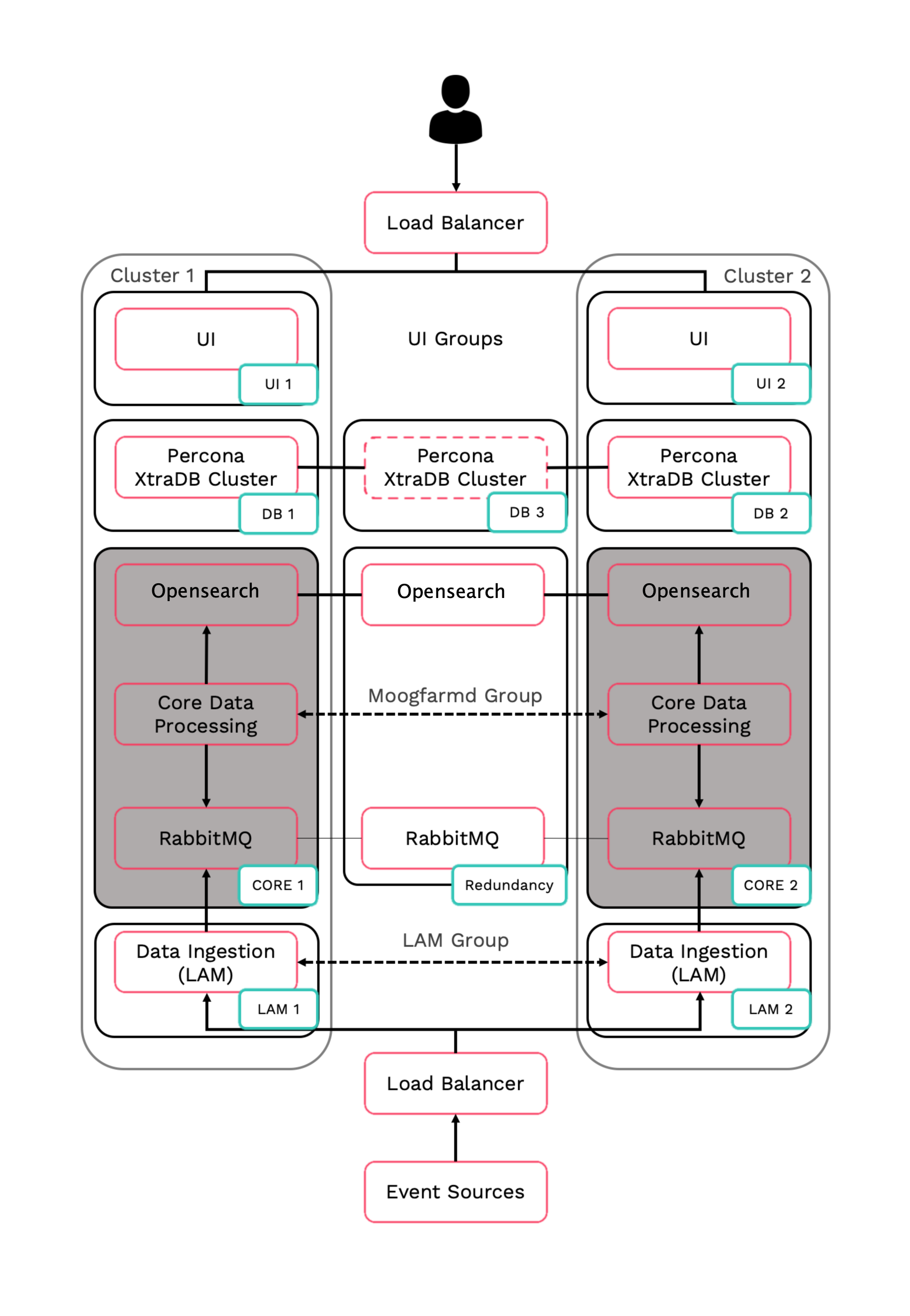
Core 1: Core Data Processing 1 (Moogfarmd), Search Node 1, RabbitMQ Node 1.
Core 2: Core Data Processing 2 (Moogfarmd), Search Node 2, RabbitMQ Node 2.
Redundancy: Search Node 3, RabbitMQ Node 3.
Refer to the Distributed HA system Firewall for more information on connectivity within a fully distributed HA architecture.
Install Core 1
Install the required Moogsoft Onprem packages:
VERSION=9.2.0; yum -y install moogsoft-server-${VERSION} \ moogsoft-search-${VERSION} \ moogsoft-common-${VERSION} \ moogsoft-mooms-${VERSION} \ moogsoft-integrations-${VERSION} \ moogsoft-integrations-ui-${VERSION} \ moogsoft-utils-${VERSION}Edit your
~/.bashrcfile to contain the following lines:export MOOGSOFT_HOME=/usr/share/moogsoft export APPSERVER_HOME=/usr/share/apache-tomcat export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/latest export PATH=$PATH:$MOOGSOFT_HOME/bin:$MOOGSOFT_HOME/bin/utils
Source the
~/.bashrcfile:source ~/.bashrc
Initialize RabbitMQ Cluster Node 1 on the Core 1 server. Substitute a name for your zone.
moog_init_mooms.sh -pz <zone>
Initialize, configure and start Opensearch. Follow the Opensearch Clustering guide here: Opensearch Clustering Guide
On Core 1, edit
$MOOGSOFT_HOME/config/system.confand set the following properties. Substitute the name of your RabbitMQ zone, the server hostnames, and the cluster names."mooms" : { ... "zone" : "<zone>", "brokers" : [ {"host" : "<Core 1 server hostname>", "port" : 5672}, {"host" : "<Core 2 server hostname>", "port" : 5672}, {"host" : "<Redundancy server hostname>", "port" : 5672} ], ... "cache_on_failure" : true, ... "search" : { ... "nodes" : [ {"host" : "<Core 1 server hostname>", "port" : 9200}, {"host" : "<Core 2 server hostname>", "port" : 9200}, {"host" : "<Redundancy server hostname>", "port" : 9200} ] ... "failover" : { "persist_state" : true, "hazelcast" : { "hosts" : ["<Core 1 server hostname>","<Core 2 server hostname>"], "cluster_per_group" : true } "automatic_failover" : true, } ... "ha": { "cluster": "PRIMARY" }Restart Opensearch (run the right command as appropriate):
systemctl restart opensearch
Uncomment and edit the following properties in
$MOOGSOFT_HOME/config/moog_farmd.conf. Note the importance of the initial comma. Delete the cluster line in this section of the file., ha: { group: "moog_farmd", instance: "moog_farmd", default_leader: true, start_as_passive: false }Start
moog_farmd:systemctl start moogfarmd
Install, configure and start HA Proxy on the Core 1 server to connect to Percona XtraDB Cluster.
Install Core 2
Install Moogsoft Onprem components on the Core 2 server.
On Core 2 install the following Moogsoft Onprem components:
VERSION=9.2.0; yum -y install moogsoft-server-${VERSION} \ moogsoft-search-${VERSION} \ moogsoft-common-${VERSION} \ moogsoft-mooms-${VERSION} \ moogsoft-integrations-${VERSION} \ moogsoft-integrations-ui-${VERSION} \ moogsoft-utils-${VERSION}Edit your
~/.bashrcfile to contain the following lines:export MOOGSOFT_HOME=/usr/share/moogsoft export APPSERVER_HOME=/usr/share/apache-tomcat export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/latest export PATH=$PATH:$MOOGSOFT_HOME/bin:$MOOGSOFT_HOME/bin/utils
Source the
~/.bashrcfile:source ~/.bashrc
On Core 2 initialize RabbitMQ. Use the same zone name as Core 1:
moog_init_mooms.sh -pz <zone>
Initialize, configure and start Opensearch. Follow the Opensearch Clustering guide here: Opensearch Clustering Guide
On Core 2, edit
$MOOGSOFT_HOME/config/system.confand set the following properties. Substitute the name of your RabbitMQ zone, the server hostnames, and the cluster names."mooms" : { ... "zone" : "<zone>", "brokers" : [ {"host" : "<Core 1 server hostname>", "port" : 5672}, {"host" : "<Core 2 server hostname>", "port" : 5672}, {"host" : "<Redundancy server hostname>", "port" : 5672} ], ... "cache_on_failure" : true, ... "search" : { ... "nodes" : [ {"host" : "<Core 1 server hostname>", "port" : 9200}, {"host" : "<Core 2 server hostname>", "port" : 9200}, {"host" : "<Redundancy server hostname>", "port" : 9200} ] ... "failover" : { "persist_state" : true, "hazelcast" : { "hosts" : ["<Core 1 server hostname>","<Core 2 server hostname>"], "cluster_per_group" : true } "automatic_failover" : true, } ... "ha": { "cluster": "SECONDARY" }Restart Opensearch (run the right command as appropriate):
systemctl restart opensearch
Uncomment and edit the following properties in
$MOOGSOFT_HOME/config/moog_farmd.conf. Note the importance of the initial comma. Delete the cluster line in this section of the file., ha: { group: "moog_farmd", instance: "moog_farmd", default_leader: false, start_as_passive: false }Start
moog_farmd:systemctl start moogfarmd
The erlang cookies must be the same for all RabbitMQ nodes. Replace the erlang cookie on Core 2 with the Core 1 erlang cookie located at
/var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie. Make the Core 2 cookie read-only:chmod 400 /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie
You may need to change the file permissions on the Core 2 erlang cookie first to allow this file to be overwritten. For example:
chmod 406 /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie
Restart the
rabbitmq-serverservice and join the cluster. Substitute the Core 1 short hostname and zone:systemctl restart rabbitmq-server rabbitmqctl stop_app rabbitmqctl join_cluster rabbit@<Core 1 server short hostname> rabbitmqctl start_app
The short hostname is the full hostname excluding the DNS domain name. For example, if the hostname is
ip-172-31-82-78.ec2.internal, the short hostname isip-172-31-82-78. To find out the short hostname, runrabbitmqctl cluster_statuson Core 1.Apply HA mirrored queues policy. Use the same zone name as Core 1.
rabbitmqctl set_policy -p <zone> ha-all ".+\.HA" '{"ha-mode":"all"}'Run
rabbitmqctl cluster_statusto verify the cluster status. Example output is as follows:Cluster status of node rabbit@ip-172-31-93-201 Basics Cluster name rabbit@ip-172-31-93-201.ec2.internal Disk Nodes rabbit@ip-172-31-93-201 rabbit@ip-172-31-85-42 rabbit@ip-172-31-93-201 Running Nodes rabbit@ip-172-31-93-201 rabbit@ip-172-31-85-42 rabbit@ip-172-31-93-201 Versions ...
Install, configure and start HA Proxy on the Core 2 server to connect to Percona XtraDB Cluster
Configure OpenSearch heap size
The minimum and maximum JVM heap sizes must be large enough to ensure that OpenSearch starts.
To set the minimum and maximum JVM heap sizes:
For RPM, edit the
/etc/opensearch/jvm.options.d/moog.optionsfile.For Tarball, edit the
$MOOGSOFT_HOME/cots/opensearch/config/jvm.options.d/moog.optionsfile.
These heap sizes must be the same value. For example, to set the heap to 4 GB:
# Xms represents the initial size of total heap space # Xmx represents the maximum size of total heap space -Xms4g -Xmx4g
If you change the heap size, you must restart OpenSearch:
For RPM, run
service opensearch restart.For Tarball, run
$MOOGSOFT_HOME/bin/utils/process_cntl opensearch restart.
Opensearch Encryption
You can enable password authentication on Opensearch by editing the $MOOGSOFT_HOME/config/system.conf configuration file. You can use either an unencrypted password or an encrypted password, but you cannot use both.
You should use an encrypted password in the configuration file if you do not want users with configuration access to be able to access integrated systems.
Enable password authentication
To enable unencrypted password authentication on Opensearch, set the following properties in the system.conf file:
"search":
{
...
“username” : <username>,
“password” : <password>,
...
}To enable encrypted password authentication on Opensearch, set the following properties in the system.conf file:
"search":
{
...
“username” : <username>,
“encrypted_password” : <encrypted password>
...
}Initialize Opensearch
Opensearch already has password authentication enabled, but other users can be added. If the admin password was already changed by moog_init_search.sh while deploying Opensearch, the script will prompt for admin account details to use to create the new users. To initialize Opensearch with password authentication, run:
moog_init_search.sh -a username:password
or:
moog_init_search.sh --auth username:password
If you run moog_init_search without the -a/--auth parameters, you will not enable password authentication in Opensearch.
See Moog Encryptor for more information on how to encrypt passwords stored in the system.conf file.
You can also manually add authentication to the Opensearch configuration. You should do this if you have your own local Opensearch installation. See the external documentation for Opensearch here https://opensearch.org/docs/latest/security-plugin/configuration/index/ for more information.
Validate that failover is working
On Core 1, confirm the moog_farmd process is active on Core 1:
ha_cntl -v
You should see output indicating that the moog_farmd process is active on Core 1. If moog_farmd process is active on Core 2, stop moog_farmd on the Core 2 and restart it on Core 1.
On Core 1, deactivate moog_farmd on the primary cluster:
ha_cntl --deactivate primary.moog_farmd
Enter "y" when prompted.
Run ha_cntl -v to monitor the moog_farmd process. You will see this process stop on Core 1 and start on Core 2.
To fail the cluster back to its default state, run the following command on Core 2 to deactivate moog_farmd on the secondary cluster:
ha_cntl --deactivate secondary.moog_farmd
On Core 1, activate moog_farmd on the primary cluster:
ha_cntl --activate primary.moog_farmd
Run ha_cntl -v to confirm that moog_farmd is active on the primary cluster.